Network Configuration
Overview
To configure the gateway network interfaces using the ESF Gateway Administration Console, select the Network option located in the System area. With this option selected, the Network display appears with a list of available interfaces. Configuration tabs for the selected interface appear on the right side of the screen.
By default, the loopback (lo) interface is selected when the network interfaces are displayed. Choose the desired network interface (e.g., eth0, eth1, wlan0, ppp0) and apply the necessary configuration changes using the tabs on the right. Submit the modified configuration by clicking the Apply button.
NOTE: It is recommended that the TCP/IP tab is configured first since it defines how the interface is going to be used.
TCP/IP Configuration
The TCP/IP tab contains the following configuration parameters:
- Status
- Disabled - disables the selected interface (i.e., administratively down).
- Enabled for LAN - designates the interface for a local network. It can be set as a DHCP server for hosts on the local network and can serve as a default gateway for those hosts; however, it cannot be set as an actual gateway interface for this device. That is, packets must be routed from this interface to another interface that is configured as WAN.
- Enabled for WAN - designates the interface as a gateway to an external network.
- Configure
- Manually - allows manual entry of the IP Address and Netmask fields, if the interface is configured as LAN; allows manual entry of the IP Address, Netmask, Gateway, and DNS Servers fields, if the interface is designated as WAN.
- Using DHCP - configures the interface as a DHCP client obtaining the IP address from a network DHCP server.
-
IP Address - defines the IP address of the interface, if manually configured.
-
Subnet Mask - defines the subnet mask of the interface, if manually configured.
-
Gateway - specifies the default gateway for the unit. (Required field if the interface is designated as WAN and manually configured.)
-
DNS Servers - provides a list of DNS servers, if the interface is designated as WAN and is manually configured.
- Search Domains - not implemented.
If the network interface is Enabled for LAN and manually configured (i.e., not a DHCP client), the DHCP & NAT tab allows the DHCP server to be configured and/or NAT (IP forwarding with masquerading) to be enabled.
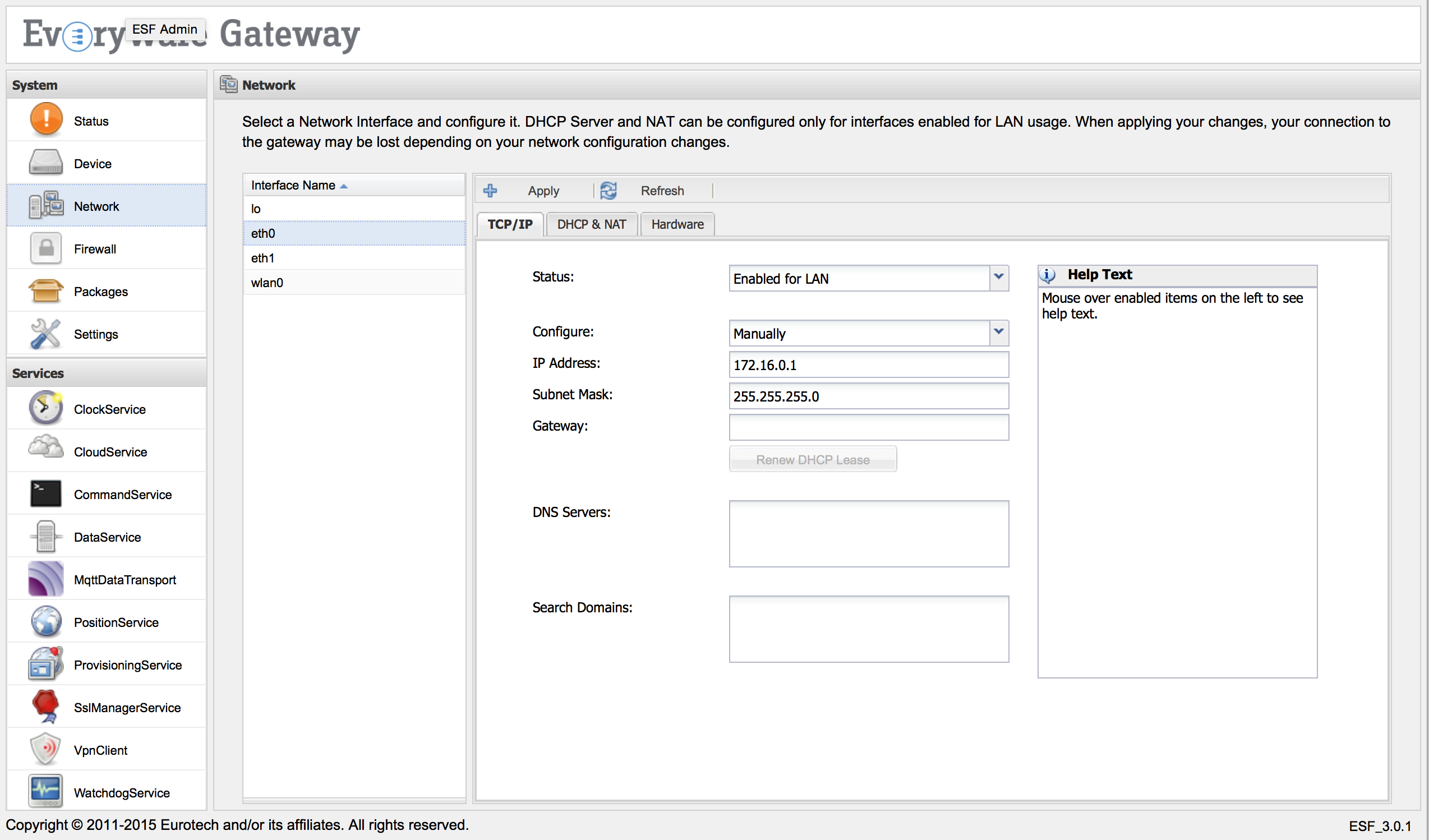
DHCP & NAT Configuration
The DHCP & NAT tab contains the following configuration parameters:
- Router Mode
- DHCP and NAT - indicates that both DHCP server and NAT are enabled.
- DHCP Only - indicates that DHCP server is enabled and NAT is disabled.
- NAT Only - indicates that NAT is enabled and DHCP server is disabled.
- Off - indicates that both DHCP server and NAT are disabled.
-
DHCP Beginning Address - specifies the first address of DHCP pool (i.e., first available client IP address).
-
DHCP Ending Address - specifies the last address of DHCP pool (i.e., last IP address that can be assigned to a client).
-
DHCP Subnet Mask - defines the subnet mask that is assigned to a client.
-
DHCP Default Lease Time - sets the default time (in minutes) that the client retains the provided IP address.
-
DHCP Max Lease Time - sets the maximum time (in minutes) that the client retains the provided IP address.
- Pass DNS Servers through DHCP - enables DNS Proxy (i.e., passing DNS servers through DHCP).
If NAT is enabled and there is another interface designated as WAN (e.g., ppp0), the following iptables rules are added to the custom automatic NAT service rules section of the /etc/init.d/firewall script:
# custom automatic NAT service rules (if NAT option is enabled for LAN interface) iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o ppp0 -j MASQUERADE iptables -A FORWARD -i ppp0 -o eth0 -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -i eth0 -o ppp0 -j ACCEPT
Also, IP forwarding is enabled in the kernel as follows:
# allow fowarding if any masquerade is defined echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
The rules shown above create an Overloaded (i.e., many-to-one) NAT. This type of network address translation maps multiple IP addresses on the LAN side to a single IP address on the WAN side, allowing internet access from hosts on a local network via a gateway (WAN) interface. Note that for NAT rules to be added, it is insufficient to enable NATing through the DHCP & NAT tab of the LAN interface; there must also be another interface designated as WAN.
Network Linux Configuration
When applying a new network configuration, ESF changes the configuration files of the Linux networking subsystem. Please read the following note before proceeding with manual changes of the Linux networking configuration.
NOTE: Eurotech does NOT recommend performing manual editing of the Linux networking configuration files when the gateway configuration is being managed through ESF. While Linux may correctly accept manual changes, ESF may not be able to interpret the new configuration resulting in an inconsistent state.
